Blood pressure and obesity: Are they related? Its adverse impacts and remedies

- advancedb_admin
- February 8, 2023
- 12:17 pm
- No Comments
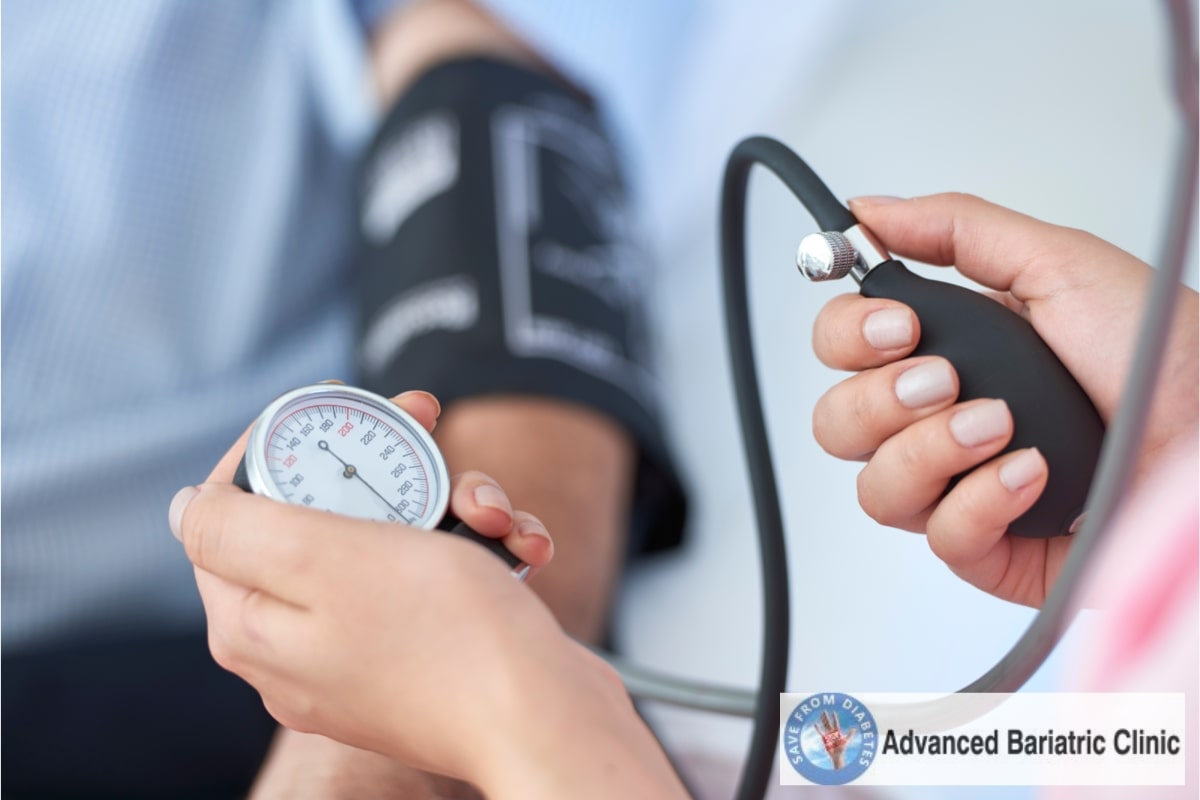
All people have blood pressure. Doctors recommend medication to control it when it is outside of normal levels since it can occasionally be a sign of heart disease.
Although blood thinners are recommended, the underlying problem of blood thickening, and fat, is hardly addressed.
So, it’s obvious that fat and daily stress contributes to high blood pressure, but nobody ever mentions the horrifyingly high levels’ root causes, which include acidic foods, processed foods, and chemicals.
Fats and salt, which thicken and restrict the arteries, are present in all animal products, including dairy. Eat more high-fiber foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds.
We frequently believe that we just add a small amount of salt to our food. But a larger part of the salt we consume actually comes from processed foods, which are heavy in salt.
Blood pressure is increased by both tea and coffee. Diabetes patients are more likely to have visceral fat, increasing their heart disease risk. Losing abdominal fat helps to stabilize blood pressure by relieving pressure on the heart.
Obesity increases the chance of developing the renal disease, essential hypertension, diabetes, and other illnesses, therefore it’s important to take any prescription medications seriously, monitor blood pressure levels, and incorporate nutrition and exercise into your daily routine for a healthier lifestyle.
Some obese people will have blood pressure readings below 140/90 mm Hg, the standard threshold for hypertension.
Water is the best beverage for maintaining healthy blood pressure because of this. Studies have indicated that adding minerals like calcium and magnesium to water will further help to lower blood pressure if you want to maximize the advantages. The American Heart Association claims that potassium reduces the effects of sodium and eases tension in the blood vessel walls. Consequently, consume foods high in potassium, such as avocado, cantaloupe, honeydew melon, fish, mushrooms, sweet potatoes, tomatoes, tuna, and beans.
Thus, we can say. BP and obesity are related.
The sixth most important determinant in the overall burden of disease in the world is excess body weight. The body mass index (BMI), which has been used to quantify obesity, is known to be biologically linked to hypertension and can be decreased through weight loss.
Body mass index (BMI) values over 30 are considered obese, which is a significant risk factor for high blood pressure. According to demographic research, obesity carries a risk of at least two-thirds of the prevalence of hypertension.
Obesity is typically defined by an increase in the quantity or size of fat cells in the body. It may be brought on by:
- The quantity and variety of meals you consume.
- The volume of exercise you get.
- Your ancestry.
- A look into your ancestry.
- The quantity and quality of your sleep.
- wearing an inappropriate or unsupported bra; a lack of female hormones
- Several pregnancies
- Breastfeeding
Your arteries are put under a lot of stress when you have excess body weight because your heart needs to work significantly harder to pump blood throughout your body. The blood pressure increases as a result of the increased arterial stress. Normal blood pressure is seen as being 120/80 mm Hg.
Obesity and Blood Pressure Effects on Kidney
Your kidneys experience stress from obesity, which ultimately increases the burden on your heart. The little blood vessels in your kidney are under additional pressure when you have high blood pressure and are overweight, which harms the organ. It becomes more difficult for your kidneys to filter your blood to remove waste and fluids when the walls of the vessels thicken. This reduces blood flow. Your heart needs to work significantly harder when your kidneys are unable to flush out extra fluid. As a result, the blood pressure keeps rising as this vicious cycle continues.
Treatment approach for obese adults with high blood pressure
By losing weight and other dietary and lifestyle changes, it is quite likely that blood pressure will be reversed or managed.
Dietary Modifications:
- Keep clear of high-calorie foods including fast food, fried foods, sweets, desserts, ice cream, and pastries.
- Because salt attracts water, eating too much of it can also make your blood pressure go up.
- Your blood vessels will retain more fluid when your blood salt levels rise, which will raise blood vessel pressure. limiting consumption of foods that are salty or rich in sodium, such as papads, pickles, chips, processed foods, French fries, restaurant cuisine, canned goods, etc. Adults are advised by the American Heart Association to limit their daily sodium intake to 1500 mg.
- All packaged foods should have nutritional labels that you should read to check for sodium content, added salt, preservatives, and monosodium.
- Consuming a caloric deficit diet of 1100–1200 calories per day, which is low in fat, high in protein, and moderate in complex carbs
- Consuming no more than 2 servings of fresh fruit each day and 4–5 servings of vegetables; • Refraining from consuming alcohol.
Recent Posts
-
 Caring for Young Warriors: Managing Diabetes in Children and Adolescents in Hyderabad
Caring for Young Warriors: Managing Diabetes in Children and Adolescents in Hyderabad -
 Demystifying Diabetes in Hyderabad: Prevalence, Causes, and Preventive Measures
Demystifying Diabetes in Hyderabad: Prevalence, Causes, and Preventive Measures -
 Balancing Tradition and Health: Traditional Hyderabadi Foods for Diabetes Managemen
Balancing Tradition and Health: Traditional Hyderabadi Foods for Diabetes Managemen -
 Navigating Diabetes in Hyderabad's Climate: Tips for Effective Management
Navigating Diabetes in Hyderabad's Climate: Tips for Effective Management -
 Why Advanced Bariatric Clinic is the Best Diabetologist in Hyderabad
Why Advanced Bariatric Clinic is the Best Diabetologist in Hyderabad


